Discitis: MRI Changes at the Endplate and Vertebral Body
In the last post we looked at the changes to the disc in discitis. This post looks at the endplate and vertebral body in acute discitis.
| WHAT TO LOOK FOR AT THE ENDPLATE? |
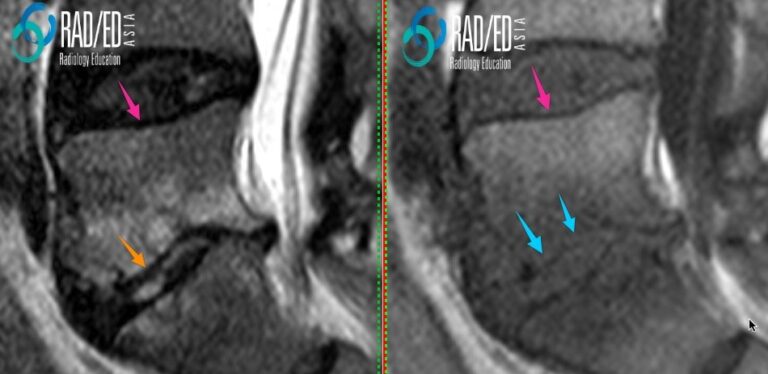
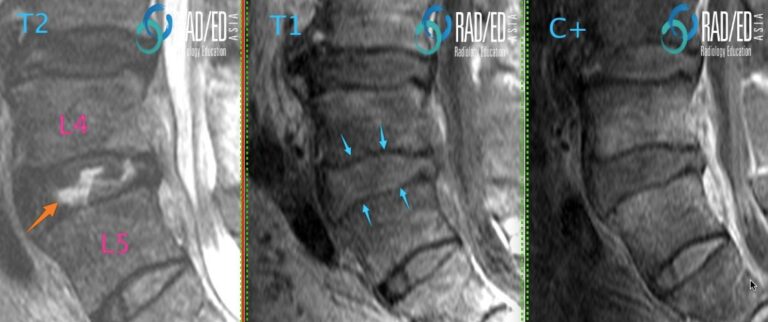
Image Above: Endplate thinning. Normal endplate ( pink arrows) is black on T1 and T2 sequences. At the inferior endplate of L5 thinning of the endplate is best appreciated on the T1 scans ( blue arrow). T2 scan endplate erosion ( orange arrow) not as prominent. WHICH SEQUENCE IS BETTER FOR DETECTING ENDPLATE CHANGES? Image Above: Established discitis at the L4/5 level. The non contrast T1 scan is usually the best sequence to appreciate the thinning of the endplate ( blue arrows) compared to the T2 and T1C+. Thi sis probably because the contrast between oedema and the the low signal of the endplate is reduced compared to the other sequences. |
| WHAT TO LOOK FOR IN THE VERTEBRAL BODY |
| 1. SUBCORTICAL OEDEMA
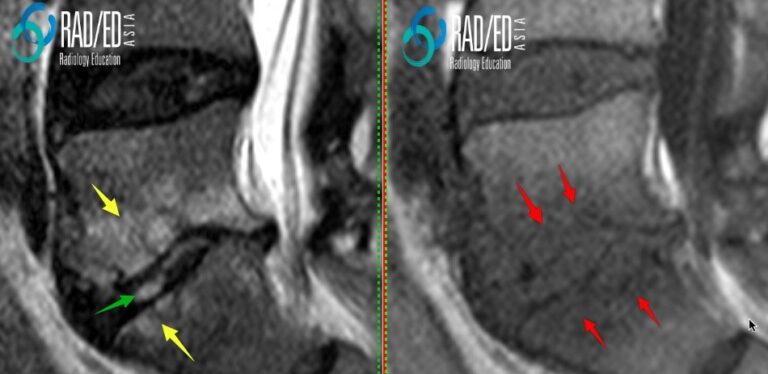
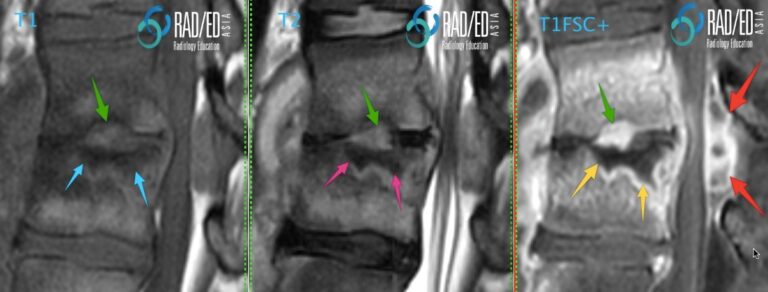
2. SUBCORTICAL CYSTIC CHANGE FROM BONE DESTRUCTION 3. BONE NECROSIS 4. INTRAOSSEOUS ABSCESS FORMATION BONE MARROW OEDEMA Image Above: Subcortical oedema in established discitis high signal T2 ( yellow arrows) and low signal T1 ( red arrows). Increased T2 signal in the disc ( green arrow) from discitis. SUBCORTICAL EROSIONS AND CYSTIC CHANGE Image above: Early subcortical “cystic” changes due to extension of infection through the destroyed endplate with subcortical bone destruction. BONE NECROSIS Image Above: Bone necrosis low signal on all sequences ( blue, pink and yellow arrows) with no enhancement. Compare with the endplate above where there is bone erosion with infective granulation tissue ( green arrows) which is high signal on T2 and enhances. Posterior epidural abscess ( red arrow).
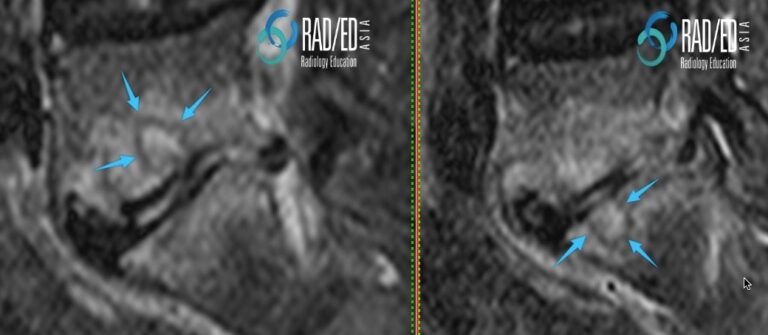
Image Above: Intra osseous abscess formation. ” Cystic” type change ( pink arrows) with no central enhancement ( blue arrows) on the C+ images. Progressive bone destruction has resulted in a non enhancing infected cavity. The high T2 signal and absence of enhancement indicates that it is fluid. Compare with the infracted bone which also doesnt enhance but is low signal on T2. |